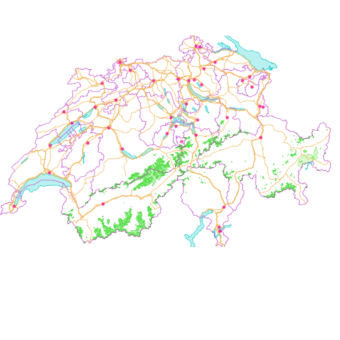
CH Swisstopo LeichteBasiskarte schema
The vector tile schema describes how the vector data is organized into different thematic layers and which attribute and values each layer contains. This is useful for writing a map style.
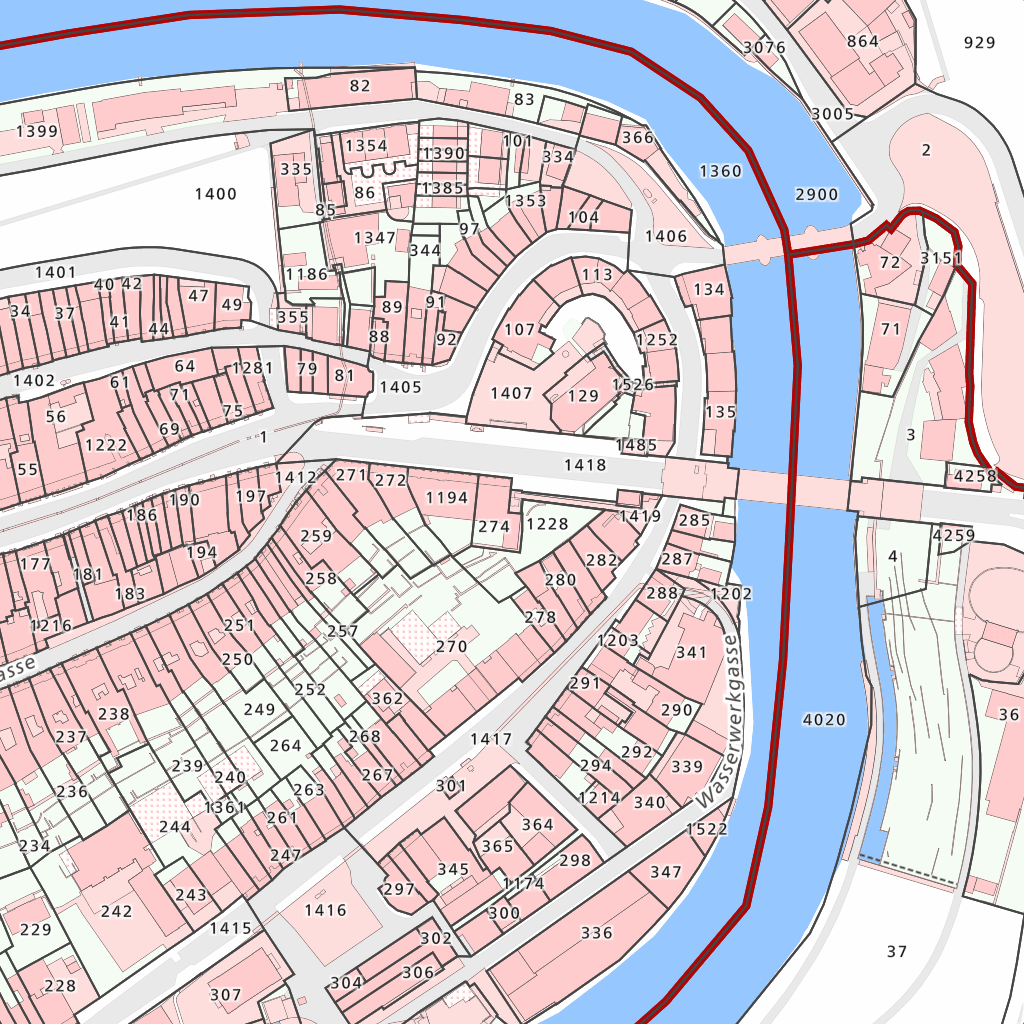
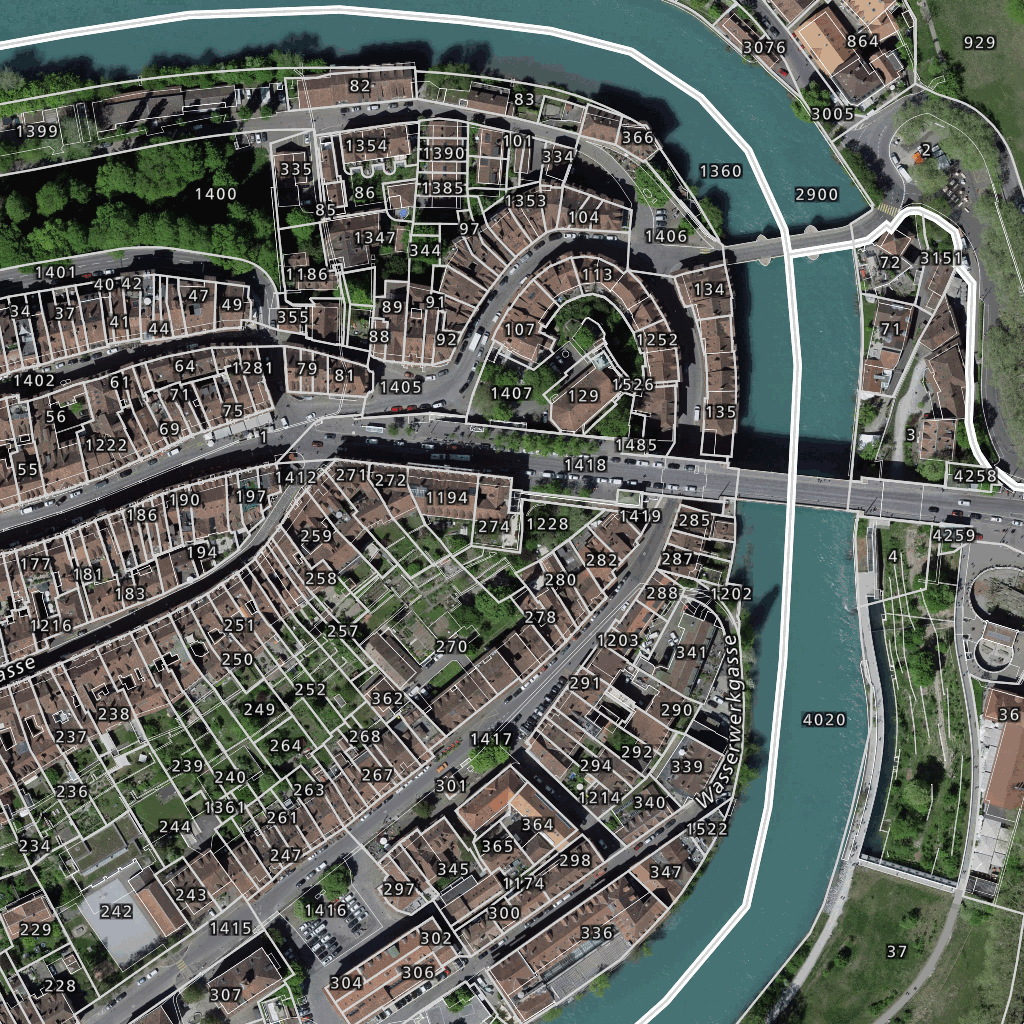
CH Swisstopo Leichte Basiskarte tileset is a tileset showcasing all SwissTopo layers.
Explore the tileset in the interactive map viewer, check the date of the last update, use it as vector tiles, etc.
Inspect CH Swisstopo LeichteBasiskarte schema
Maps with this tileset
Definition of layers
The CH Swisstopo LeichteBasiskarte tileset contains the following layers:
aerodrome_label #
Fields
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
class
Distinguish between more and less important aerodromes.
Possible values:
internationalhelipadregionalother
ele
elevation in meters, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
ele_ft
elevation in feet, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
iata
iata-code
icao
icao-code
aeroway #
Airport buildings are contained in the building layer but all other airport related polygons can be found in the aeroway layer.
Fields
class
polygon of surfaces used for aerial operations
Possible values:
runwayrunway_grass
area_name #
area_name layer for the LBM, contains points and lines for labelling areas.
Fields
class
area names
Possible values:
place
subclass
different classes of areas
Possible values:
massifglacier
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
boundary #
Contains administrative boundaries as linestrings.
Fields
admin_level
admin_level indicating the level of importance of this boundary.
The admin_level corresponds to the lowest admin_level the line participates in.
adm4_l
the name of the administrative unit with admin_level = 4 to the left side of the boundary (canton name) or if it is an enclave (foreign territory) the name of the country. can be used to label boundaries.
adm4_r
the name of the administrative unit with admin_level = 4 to the right side of the boundary (canton name) or if it is an enclave (foreign territory) the name of the country. can be used to label boundaries.
disputed
wether the boundary is disputed or not
maritime
wether the boundary is in the sea or not
building #
buildings including roofs without sidewalls
Fields
render_height
the average height of a building
render_min_height
the height of the bottom of the building
building_ln #
building_line layer for the LBM
Fields
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
class
Distinguish between classes of geometries.
Possible values:
horse_racingski_jumptoboggantrackweir
construct #
manmade structures not suitable for the layer building.
Fields
class
use class to differentiate between different manmade structures.
Possible values:
damlockplatform
contour_line #
contour lines
Fields
class
use class attribute to assign differnt colors for contour_lines.
Possible values:
landicescreewater
ele
elevation in meters, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
ele_ft
elevation in feet, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
landcover #
Landcover is used to describe the physical material at the surface of the earth.
Fields
class
Use the class to assign natural colors for landcover.
Possible values:
farmlandicewoodrockgrasswetland
subclass
Use subclass to do more precise styling.
Possible values:
allotmentsforestloose_forestglaciergolf_courseorchardparkplant_nurseryscrubswampvineyardwoody_plant
landuse #
Landuse is used to describe use of land by humans.
Fields
class
Use the class to assign special colors to areas.
Possible values:
cemeterylandfillparkingpitchquarry
mountain_peak #
peaks or other topographical landmarks.
Fields
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
class
Use the class to differentiate between different topographic landmarks.
Possible values:
alpine_peakmain_peakpeakmain_hillhillrocky_knollmountain_passsaddle
ele
elevation in meters, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
ele_ft
elevation in feet, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
rank
values of 1-5 according to relevance of a peak with more important peaks having lower rank values. can be used to adapt styling and filter mountain_peaks with lower values.
park #
The park layer contains parks from national park and protected areas. contains polygons for area and points for labelling
Fields
class
Use the class to differentiate between different parks.
Possible values:
national_park
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
place #
used to label places.
Fields
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
capital
The capital field marks the
admin_level
of the boundary the place is a capital of.
Possible values:
24
class
distinguish between different size and importance of labelled places.
Possible values:
countrycitytownvillagehamletisolated_dwellingneighbourhoodsuburbisland
iso_a2
Two-letter country code ISO 3166-1 alpha-2.
code
Two-letter canton code.
population
Approximate number of inhabitants. Can be used to prioritize labelling. Data is not validated and may not be used for analysis!
rank
Use rank to boost importance of places on the map.
Important places have lowar ranks than less important ones.
The rank field for counries IS 1.
The rank field for cities ranges from 3 to 4.
places gruadually rank higher serially based on the
local importance of the place with higher ranks being less important.
You can use the rank to limit density of labels or improve
the text hierarchy.
poi #
LBM POIs
Fields
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
class
More general classes of POIs. If there is no more general class for the subclass
this field will contain the same value as subclass.
Possible values:
aerialwayallotmentsattractionboundary_stonebuildingbuscampsitecastlecavecemeterycollegedamdolineelevatorferry_terminalfuelfuniculargolfhospitallocklodgingmilitarymonasterymonumentmotorwayparkpitchplace_of_worshippowerprisonrailwayruinsschoolsports_centrespringstadiumstonestorage_tanksurvey_pointswimming_pooltowerwastewater_plantwaterfallweirzoo
subclass
More refined description.
Possible values:
aerialway_stationallotmentsalpine_hutantenna_areaattractionboundary_stonebuildingbus_stopcable_car_stationcamp_sitecaravan_sitecar_ferrycastlecavecemeterychair_lift_stationchristianchurch_towercollegecommunications_towerdamdriving_centreelevatorentry_exitexitfairgroundferryferry_terminalfunicular_stopgolf_coursegondola_stationhorse_racinghospitalincineration_plantjunctionlockmilitarymonumentobservation_towerobservatoryparkpower_plantprisonrailway_stationrest_arearestaurantrest_stopruinsschoolshopsports_centrespringstadiumstone_subway_stopsurvey_pointsurveying_pyramidswimming_pooltowertoiletstram_stopuniversityviewpointwastewater_plantwaterfallwater_tankweirwilderness_hutwind_turbinezoo
direction
can be used to orientate direction for waterfalls
spot_elevation #
spot elevation.
Fields
class
class can be used to allow different styling of elevation points.
Possible values:
spot_elevationterrain_spot_elevationlake_elevationsinkholesinkhole_rocksinkhole_screesinkhole_icesinkhole_waterdoline
ele
elevation in meters, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
ele_ft
elevation in feet, measured in reference system LV95, srid 2056.
lake_depth
the maximum depth of the lake in meters.
lake_depth_ft
the maximum depth of the lake in feet.
transportation #
transportation contains roads, railways, aerialways, and ferry lines. It contains all roads from motorways to primary, secondary and tertiary roads to residential roads and foot paths. Styling the roads is the most essential part of the map.
Fields
class
Distinguish between more and less important roads, railways, shipways and aerialways.
Possible values:
motorwaytrunkprimarysecondarytertiaryminorpathfootwayservicetracktrailtransitrailvia_ferrataferrycar_ferrycable_cargondolachair_lift
subclass
Distinguish more specific qualities.
Possible values:
avalanche_protectoravalanche_protector_bridgecovered_bridgestepstramsubwayfunicularrailrack_railnarrow_gauge
brunnel
Mark whether it is a bridge or tunnel or ford.
Possible values:
bridgetunnelford
ramp
Mark with 1 whether way is a ramp (link or steps)
or not with 0.
Possible values:
01
oneway
Trafficways that are not oneway are marked with 0, oneway trafficways are marked with 1 and duplicate road tunnel oneways may be marked with 2 for filtering at lower zoomlevels.
Possible values:
012
layer
Used to describe vertical relationships between crossing or overlapping features.
Possible values:
-5-4-3-2-112345
surface
Used to describe the surface type of roads.
Possible values:
pavedunpaved
sac_scale
Different kinds of hiking trails.
Possible values:
mountain_hikinghikingalpine_hiking
service
Mark railways that are dead-ends.
Possible values:
siding
is_route
Mark roads that are important routes (values 5-10) or main railways (value 99).
Possible values:
56781099
transportation_name #
Labeling geometry for transportation layer.
Fields
class
Distinguish between more and less important roads or railways and roads.
Possible values:
motorwaytrunkprimarysecondarytertiaryminorpathservicetracktrailtransitrailvia_ferrataferrycar_ferrycable_cargondolachair_lift
subclass
Distinguish more specific qualities.
Possible values:
avalanche_protector_bridgecovered_bridgestepstramsubwayfunicularrailrack_railnarrow_gauge
brunnel
Mark whether it is a bridge or tunnel or ford.
Possible values:
bridgetunnelford
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
ref
Route number.
ref_length
Length of ref field.
layer
Used to describe vertical relationships between crossing or overlapping features.
Possible values:
-5-4-3-2-112345
is_route
Mark roads that are important routes (values 5-10) or main railways (value 99).
Possible values:
56781099
water #
Water polygons representing rivers and lakes but also artificial constructions such as pools
Fields
class
Water bodies are classified as lake, river or pool.
Possible values:
lakeriverpool
water_name #
The water_name layer contains points to label waterbodies.
Fields
class
used to distinguish entire or parts of waterbodies.
Possible values:
lake
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
direction
direction of the lake to rotate label.
size
values 1 to 10, can be used for label size.
waterway #
Lines of waterways or outlines of waterbodies. Underground waterways are not included.
Fields
name
common name
name:latin
common name, latin alphabet
name:de
german name, if unavailable uses default name
name:fr
french name, if unavailable uses default name
name:it
italien name, if unavailable uses default name
name:rm
romansh name, if unavailable uses default name
class
stream/river are classified by Strahler-order. Upstream rivers are classified as streams, once they reach a certain Strahler number or if they intersect with a waterbody (polygon), they are classified as rivers.
Possible values:
streamriverpressuriseddrain
intermittent
Mark with 1 if it is an intermittent waterway.
Possible values:
01
width
used to symbolize downstream rivers wider than upstream.
License
With the use of this API, you must visibly credit these attributions: